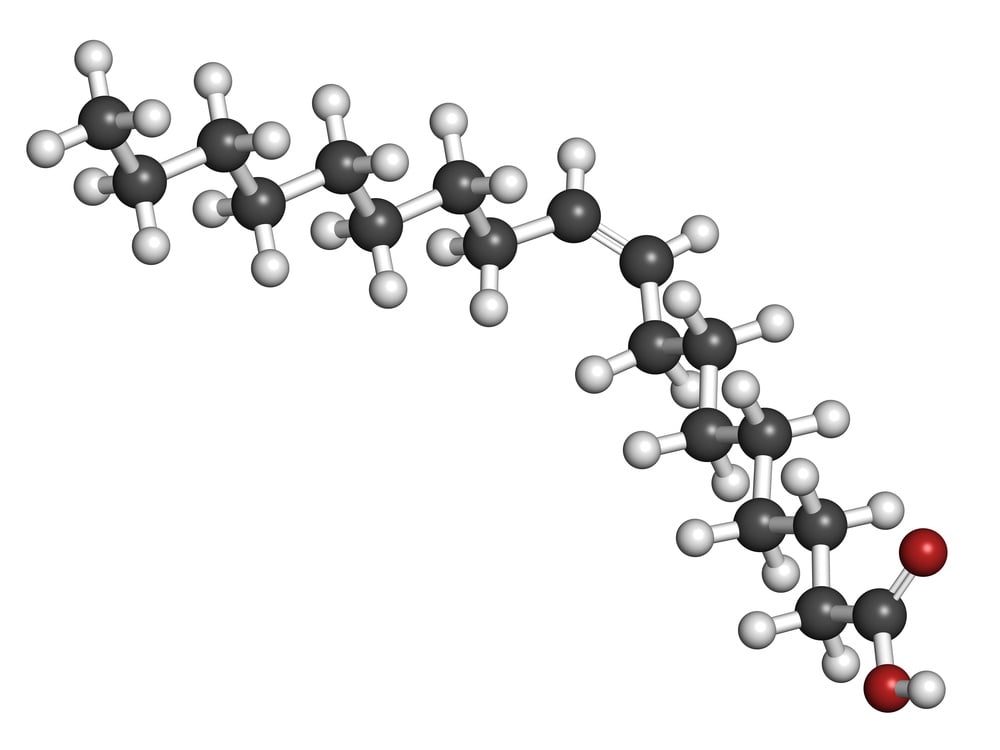
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid. Some oils, such as olive oil, are naturally high in oleic acid. Extra virgin olive oil, olive oil and extra light tasting olive oil are all naturally high oleic. In fact, oleic acid is named after olive oil.
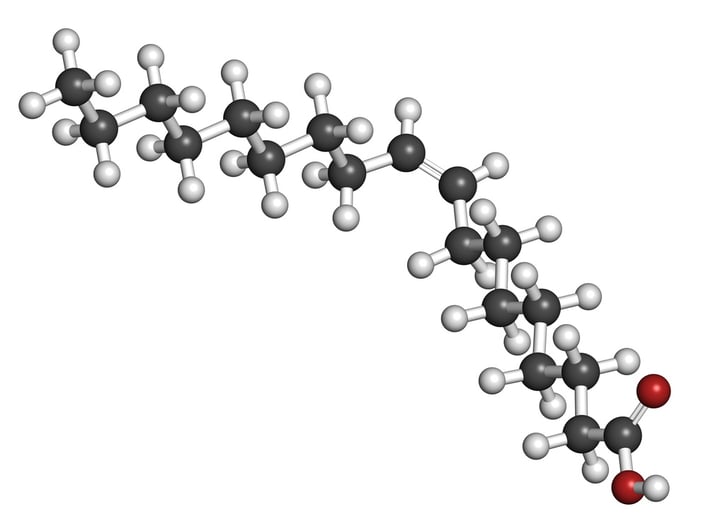
Oleic acid is highly desirable from a health perspective. Oleic acid has been found to lower blood pressure and cholesterol. Oleic acid has also been found to raise HDL (good) cholesterol, fight inflammation and fight the effects of free radicals in the body.
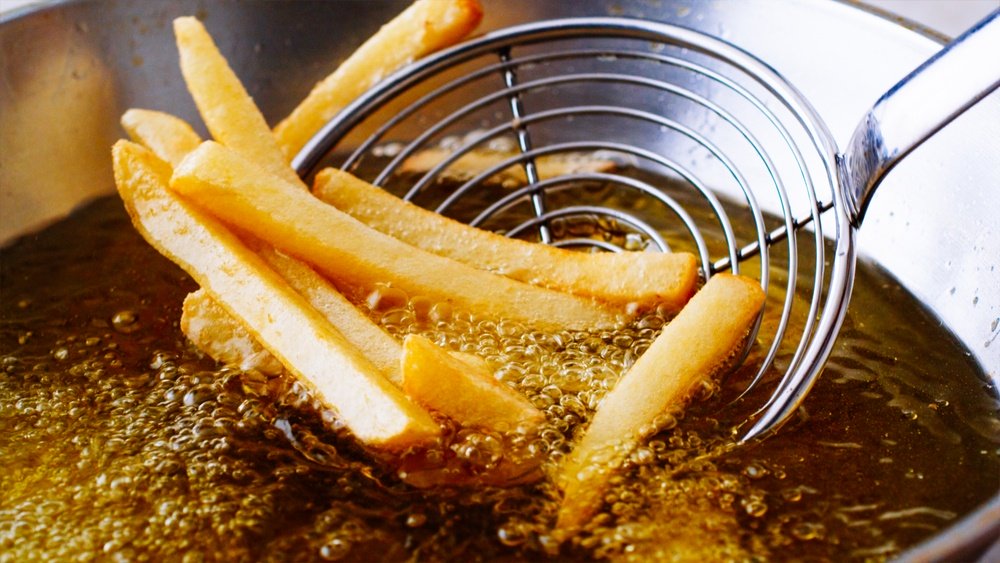
High oleic oils are also highly desirable to food manufacturers and in the restaurant industry. Oleic acid is stable at room temperature and resists rancidity. Oleic acid also can endure heating without breaking down.
While olive oil is naturally high oleic, some seed oils have been hybridized or genetically modified to change their oleic acid content. These oils include soybean, canola and sunflower oils.
Consumers looking to include high oleic fats in their diet should read labels carefully. Not all soybean, canola or soybean oils are high oleic. Unless the bottle is labeled as high oleic, consumers should assume that the oil that they find in their supermarket is conventional oil. Olive oil, on the other hand, is always high oleic.